1. Retrieving DNS Information
dnscmd includes
several commands you can use to retrieve information about the server,
zones, and records. The following table shows these commands.
| dnscmd Commands to Retrieve Information | Comments |
|---|
Retrieve information on the DNS server.
/info
dnscmd [server] /info
c:\>dnscmd /info
c:\>dnscmd dc1 /info
| Retrieves
information on the DNS server including server-level properties.
You can include the name of a remote server by adding the name of the
server, or you can execute it on a local DNS server and omit the server
name. |
List zones.
/enumzones
dnscmd [server] /enumzones
c:\>dnscmd /enumzones
c:\>dnscmd dc1 /enumzones
| You can enumerate (or list) zones on a DNS server with the /enumzones switch. |
Retrieve performance statistics.
/statistics
dnscmd [server] /statistics
c:\>dnscmd /statistics
c:\>dnscmd dc1 /statistics
| The /statistics switch shows performance statistics for the DNS server. |
Retrieve information on a zone.
/zoneinfo
dnscmd /zoneinfo zonefqdn
filename
c:\>dnscmd /zoneinfo
pearson.pub
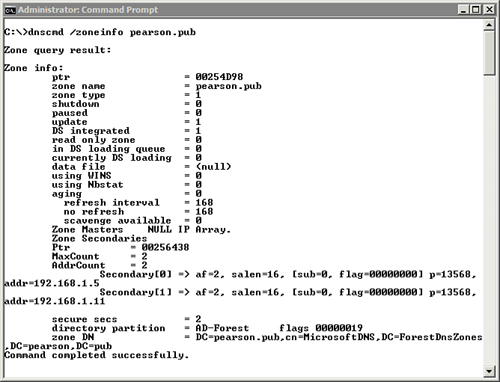
| The /zoneinfo
switch retrieves information on a specific zone, including the
properties of the zone. Much of this information is coded. For example, a
zone type of 1 indicates it is a primary zone and a 1 for DS integrated
indicates it is Active Directory integrated (ADI). Figure 5-1 shows the output of this command. |
List records in zone.
/enumrecords
dnscmd server /enumrecords
zonename zonenode
c:\>dnscmd dc1 /enumrecords
pearson.pub @
| You can list all records in a zone with the /enumrecords switch. The @ symbol specifies that all the records from the zone root are listed.
Tip
The output can be quite extensive. You can redirect the output to a text
file with the redirect symbol (>) and the name of a file like this:
dnscmd dc1 /enumrecords pearson.pub @ > dns.txt
|
2. Exporting DNS Data
You might occasionally want to create text files that include all the data from a zone. You can create them with the /zoneexport switch.
| Using /zoneexport | Comments |
|---|
/zonexport
dnscmd /zoneexport zonefqdn
filename
c:\>dnscmd /zoneexport
pearson.pub pearsonzone.txt
| Creates
copies of the zone data as a file. The file can then be kept for
archiving purposes or shared with other IT professionals (such as
auditing and security personnel). |
Note
The exported file is created in the windows\system32\dns folder by default.
3. Forcing Zone Transfers
Zone transfers occur on a regular schedule. When
primary and secondary DNS servers are used, zone transfer schedules are
based on settings in the Start of Authority (SOA) record. When ADI zones
are used, zone transfers occur when Active Directory replication
occurs. However, you can force zone transfers at different times.
| Forcing Zone Transfer Commands | Comments |
|---|
Update secondary DNS server.
/zonerefresh
dnscmd server /zonerefresh zone
c:\>dnscmd dc1 /zonerefresh
pearson.pub
| Forces
a zone transfer from a primary DNS server to a secondary DNS server.
You need to specify the server hosting the primary zone and the zone to
transfer. In this example, the DC1 is the DNS server and the zone name
is pearson.pub. |
Update ADI zone data.
/zonereupdatefromds
dnscmd server / zoneupdatefromds
zone
c:\>dnscmd dc1 /zoneupdatefromds
pearson.pub
| Forces
a zone transfer from directory services (for an ADI zone). This works
for any ADI zone, including those hosted on read-only domain controllers
(RODC).
Tip
When performing a zone transfer to update an RODC, run the command on a server that is not RODC.
|